-
Address: Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China, 215000
-
Tel: 0086-512-68235075
Linear Ball Bearing Block vs Linear Roller Bearing Block

In the linear transmission system, linear bearing blocks is an indispensable part, and in the classification of linear bearing blocks, and can be based on the ball in the linear bearing block divided into linear ball bearing block and linear roller The classification of linear bearing blocks can be divided into linear ball bearing block and linear roller bearing block according to the balls in the linear bearing block, many readers are confused about the distinction between these two types of linear bearing blocks, so this article will introduce the difference between linear ball bearing block and linear roller bearing block in detail, which will help to better clarify the relationship between them.
Differences between structure and operation
linear ball bearing block
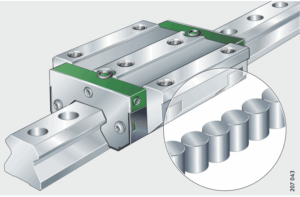
- linear ball bearing block adopts spherical ball as the rolling body, the ball has contact with the guide rail through the point contact method (two-point or four-point contact). The ball rolls in the circulating track, and due to the rolling friction brought about by the friction force is greatly reduced, so most of the well-known brands, such as PMI, Rexroth linear bearing ball block accuracy is generally in the micron level, and the slider running speed is very fast. And rolling friction wear is very small, so most of the cases of processing machine tools can be maintained for a long time accuracy.
- It is worth mentioning that, thanks to the rolling friction principle of linear ball roller block, the friction generated is small, so only a small amount of power is needed to make the linear platform run, in most cases, most of the processing machine tools need to do reciprocating motion back and forth, in this case, linear ball roller block can better reduce the energy loss of the linear platform, in addition, thanks to the friction is very small, linear ball bearing block produces less heat, which can ensure that this linear platform run for a long time. In this case, the linear ball bearing block can better reduce the energy loss of the linear platform, reduce costs and increase efficiency. In addition, since the friction is very small, the LM block produces less heat, which ensures that this LM Guide can operate for a long time.

linear roller bearing block
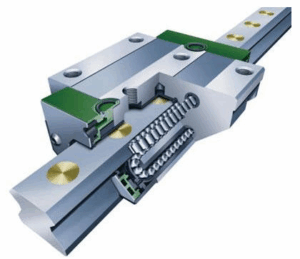
- linear roller bearing block adopts cylindrical roller as the rolling body, and linear rails to form line contact, the contact surface is rectangular or long strip, the contact surface is 10-50 times larger than the ball, which means that the large weight of items in the average unit, the area of load distribution is more uniform, so that the load is distributed along the length of the roller, unit area pressure is significantly reduced. Particularly suitable for heavy or partial load conditions, but the same caused by the slowdown, but in this case, the characteristics of the roller can be greatly improved, the line contact structure of the local load is not sensitive to the impact load can be effectively absorbed to reduce the risk of surface damage, and extend the service life.
- Linear roller bearing blocks exhibit higher heat generation than linear ball bearing blocks due to their unique line contact characteristics. However, the rigidity of the roller slider contributes to enhanced overall structural stability and superior resistance to thermal deformation.
Lubrication status and temperature characteristics
Lubrication characteristics of both
For both linear ball bearing blocks and linear roller bearing blocks, when the load increases, the lubricating grease of both will be subjected to greater stress and will age very quickly. If the premature destruction of the grease structure affects the operating performance of the grease, the grease’s life is reduced, and relubrication must be carried out in advance. If the relubrication interval is not shortened, the operating life of the linear guidance system will be affected. As grease life is shortened, the life of the linear guidance system is also reduced.
The linear ball bearing block generally requires a low viscosity lubricant to maintain the flexibility and friction of the point contacts and to maintain high speed performance and accuracy. linear ball bearing blocks generate a lot of heat from the point contact friction and are susceptible to lubricant volatilization, so if proper and timely lubrication is not provided, friction between the rollers and the linear rail will be high, and the linear ball bearing block will not function properly. If there is no proper and timely lubrication, the friction between the roller and linear bearing block will increase, which may increase the wear and reduce the lifetime, and even have the possibility of rusting.
Linear roller bearing blocks are generally lubricated with high-viscosity grease to enhance the film strength in the line contact area to withstand higher loads. Linear contact has better heat dissipation and slower lubricant consumption, but if there is no lubrication in place, there will still be no small damage to the linear roller bearing block, for example, in the case of heavy loads, due to the increase in the contact area, insufficient lubrication is easy to lead to the roller and the guideway surface adhesion wear.

Two different ways to use the application.
Linear ball bearing block: CNC machine tools, 3D printers, medical machines, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, processing machines that rely on low friction and high repetitive positioning accuracy, and machine tools, etc.
Linear roller bearing block: Machines like CNC machining centers, injection molding machines, and heavy-duty machine tools need to be able to handle high loads.
Conclusion
A comparison of linear ball bearing blocks and linear roller bearing blocks reveals that each type possesses a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. It is imperative to recognize that a single linear block does not possess the capability to fully substitute for another type of linear block. The selection of the most appropriate product necessitates a precise alignment with the particular characteristics of the specific situation under consideration.
1. What is the core structural difference between linear ball bearing blocks and roller bearing blocks?
Linear Ball Bearing Block : Uses spherical balls as rolling elements, forming point contact (e.g., two-point or four-point contact) with the guide rail.
Linear Roller Bearing Block : Uses cylindrical rollers , creating line contact with the guide rail (larger contact area).
Impact : Point contact reduces friction for high-speed applications, while line contact distributes loads more evenly for heavy-duty use.
2. Which applications are best suited for linear ball bearing blocks?
Equipment requiring high-speed operation and precision positioning (e.g., CNC machine tools, 3D printers, semiconductor manufacturing).
Light/medium-load scenarios sensitive to frictional wear (e.g., medical devices, automated production lines).
Reason : Ball bearings minimize friction and heat generation, maintaining long-term accuracy.
3. When should I choose linear roller bearing blocks?
Heavy or uneven loads (e.g., injection molding machines, heavy-duty machining centers).
Environments with shock loads or requiring resistance to thermal deformation .
Reason : Line contact distributes pressure uniformly, reducing sensitivity to localized loads and enhancing rigidity.
4. How do their lubrication requirements differ?
Linear Ball Bearing Blocks :Require low-viscosity lubricants to reduce friction and maintain high-speed performance.
Shorter relubrication intervals (heat from point contact accelerates lubricant degradation).
Linear Roller Bearing Blocks :Need high-viscosity lubricants to strengthen the oil film in line contact areas.
Longer relubrication intervals (better heat dissipation), but require monitoring under heavy loads.
5. How to choose between them based on load type?
Light/Medium Loads + High Speed : Prioritize linear ball bearing blocks (low friction, high precision).
Heavy/Impact Loads : Choose linear roller bearing blocks (superior load distribution and durability).
Note : For fluctuating or uneven loads, roller bearings offer better stability.